Compare and contrast web applications with web services
Below is the difference between web service and web application
Web Applications:
Applications that are accessed through browsers are web applications and it is the collection of multiple web pages. These are basically dependent on client server architecture where browser acts as a client which sends the request to server. Afterwards, web pages are rendered as per responses from the server. Purpose of web services is communications between various programs and applications.
During building any web application, order of focus is on:
- UI portion[Front end implementation]
- Functional portion[Back end implementation]
Web services:
Web services are mainly used to communicate the information between two systems ignoring UI interaction. Messages are transferred from one application to another application via JSONS and XMLs etc.
Web services are mainly dependent on back end implementation, UI doesn’t have any space. Clients can access only exposed methods of any functionality. Majority of the qa testing services are focusing on automating the web services to speed up the testing for integrated applications.
Web services are constructed basically to hide the implementation of any product and APIs are exposed to perform specific functions. Web services leads to many advantages for various software testing companies mentioned below:
- Re-usability of any code
- Reduced the Complexity
- Enhanced the features of any product
- Impact on cost
- Speed
Web Application :-
User-to-program interaction ,
Static integration of components ,
Monolithic service ,
Ad hoc or proprietary protocol
Web Services :-
Program-to-program interaction ,
Dynamic integration of components ,
Service aggregation (micro-services) ,
Interoperability (RPC/SOAP/REST)
What is WSDL …
WSDL (Web Services Description Language) is an XML format for describing network services as a set of endpoints operating on messages containing either document-oriented or procedure-oriented information. The operations and messages are described abstractly, and then bound to a concrete network protocol and message format to define an endpoint.
WSDL Usage :- WSDL is an XML-based interface description language that is used for describing the functionality offered by a web service. The acronym is also used for any specific WSDL description of a web service (also referred to as a WSDL file), which provides a machine-readable description of how the service can be called, what parameters it expects, and what data structures it returns. Therefore, its purpose is roughly similar to that of a type signature in a programming language.

Fundamental properties of a WSDL document
Specifies three fundamental properties:
- What a service does -operations (methods) provided by the service
- How a service is accessed -data format and protocol details
- Where a service is located -Address (URL) details
The document written in WSDL is also simple called a WSDL (or WSDL document).
WSDL is a contract between the XML(SOAP) Web service and the client who wishes to use this service.
The service provides the WSDL document and the Web service client uses the WSDL document to create the stub (or to dynamically decode messages.
WSDL document structure
The diagram below illustrates the elements that are present in a WSDL document, and indicates their relationships.
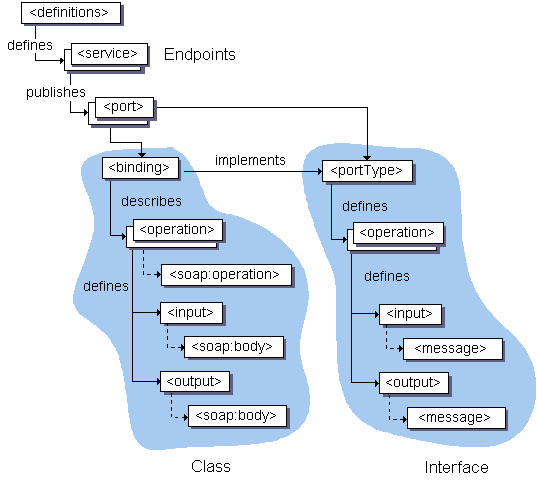
Elements in WSDL
A WSDL document has a definitions element that contains the other five elements,They are types, message, portType, binding and service. The following sections describe the features of the generated client code.
types:-
Provides information about any complex data types used in the WSDL document. When simple types are used the document does not need to have a types section.
message:-
An abstract definition of the data being communicated. In the example, the message contains just one part, response, which is of type string, where string is defined by the XML Schema.
portType:-
An abstract set of operations supported by one or more endpoints.
binding:-
Describes how the operation is invoked by specifying concrete protocol and data format specifications for the operations and messages.
service:-
Specifies the port address(es) of the binding. The service is a collection of network endpoints or ports.

The PortType and operation elements in WSDL with the java equivalences
PortType element may have one or more operation elements, each of which defines an RPC- or documentstyle Web service method
• Java equivalence:
portType -> java interface
operation -> method name
Compare and contrast the binding and service elements in WSDL
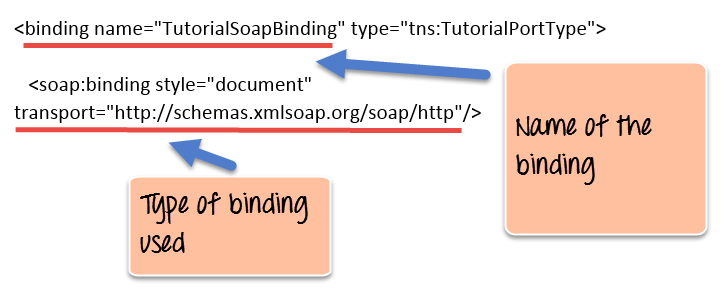
Binding…
Map a PortTypeto a specific protocol, typically SOAPover http, using a specific data encoding style .
One portTypecan be bound to several different protocolsby using more than one port .
Bindings refer back to portTypesby name, just as operations point to messages .
Binding styles may be either “RPC” or “Document”(SOAP) .
Also specify SOAP encoding .
Services…
It binds the Web service to a specific network-addressable location, i.e. it takes the bindings declared previously and ties them to a port, which is a physical network endpoint to which clients bind over the specified protocol, contain one or more port elements, each of which represents a different Web service and the port element assigns the URL to a specific binding
Reference a particular binding, and along with addressing information is wrapped together into a service element to form the final physical, network addressable Web service
Access point for each port
- port type -The operations performed by the web service.
- message -The messages used by the web service.
- types -The data types used by the web service.
- binding -The communication protocols used by the web service
How SOAP is used with HTTP
All the browsers supports HTTP for compatibility and its the most widely used Internet Protocol.A SOAP method is an HTTP request/HTTP response that compiles with the SOAP encoding rules. using SOAP, a protocol submitted to the W3C data can be enclosed in XML and transmitted using any number of Internet Protocols.
How SOAP can be used for functional oriented communication
All communication by SOAP is done via the HTTP protocol. Prior to SOAP, a lot of web services used the standard RPC (Remote Procedure Call) style for communication. This was the simplest type of communication, but it had a lot of limitations.
Let’s consider the below diagram to see how this communication works. In this example, let’s assume the server hosts a web service which provided 2 methods as
- GetEmployee – This would get all Employee details
- SetEmployee – This would set the value of the details like employees dept, salary, etc. accordingly.
In the normal RPC style communication, the client would just call the methods in its request and send the required parameters to the server, and the server would then send the desired response.

The above communication model has the below serious limitations
- Not Language Independent – The server hosting the methods would be in a particular programming language and normally the calls to the server would be in that programming language only.
- Not the standard protocol – When a call is made to the remote procedure, the call is not carried out via the standard protocol. This was an issue since mostly all communication over the web had to be done via the HTTP protocol.
- Firewalls – Since RPC calls do not go via the normal protocol, separate ports need to be open on the server to allow the client to communicate with the server. Normally all firewalls would block this sort of traffic, and a lot of configuration was generally required to ensure that this sort of communication between the client and the server would work.
To overcome all of the limitations cited above, SOAP would then use the below communication model

- The client would format the information regarding the procedure call and any arguments into a SOAP message and sends it to the server as part of an HTTP request. This process of encapsulating the data into a SOAP message was known as Marshalling.
- The server would then unwrap the message sent by the client, see what the client requested for and then send the appropriate response back to the client as a SOAP message. The practice of unwrapping a request sent by the client is known as Demarshalling.
Structure of SOAP message in message oriented communication
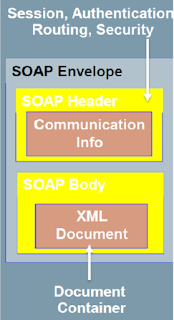
Envelope
wraps entire message and contains header and body
defines an overall framework for expressing what is in a message; who should deal with it, and whether it is optional or mandatory
Header
optional element with additional info such as security or routing
Body
application-specific message content being communicated as arbitrary XML payloads in the request and response messages
fault element provides information about errors that occurred while processing the message
The importance of the SOAP attachments
SOAP messages may have one or more attachments
Each AttachmentPartobject has a MIME header to indicate the type of data it contains.
It may also have additional MIME headers to identify it or to give its location, which can be useful when there are multiple attachments
When a SOAP message has one or more AttachmentPartobjects, its SOAPPartobject may or may not contain message content
Annotations in JAX-WS, providing examples of their us
- JAX-WS (Java API for XML Web Services) is a java package/library for developing web services
- It supports both Functional oriented and message oriented communication via SOAP
- JAX-WS API hides the complexity of SOAP from the application develope
- JAX-WS uses the javax.jwspackage
- It uses annotations
@WebService @WebMethod @OneWay @WebParam @WebResult
Web service can be tested using different approaches
Testing of web services is one of the important type of software testing approach, which is mainly used to determine the expectations for reliability, functionality, performance, etc.
As these days Automated testing is considered as one of the most trending methodology in the field of software testing, hence testing web apps based on RESTful APIs through automation will provide effective test results. Some of the best & popular tools for web services testing are:
- SoapUI,
- TestingWhiz,
- SOATest
- TestMaker,
- Postman, etc.